Glass fuses and ceramic fuses manufacturer and distributor
Discover our selection of glass and ceramic fuses
Difference between a glass fuse and a ceramic fuse
Glass fuse
Glass fuses have a transparent body, allowing you to see if the fuse has blown, making visual inspection easy.
Ceramic fuse
In contrast, ceramic fuses are opaque and typically filled with sand, which enhances their arc-quenching capabilities, allowing them to handle higher interrupting ratings and making them more suitable for high-current applications.
This is how glass fuse and ceramic fuse works
Glass and ceramic fuses both function by using a thin fuse link that melts when an overcurrent generates excessive heat, breaking the circuit to prevent damage. Ceramic fuses, unlike glass fuses, are filled with sand, which enhances their arc-quenching capability by absorbing heat and containing any arcs that may form when the fuse blows, making them more suitable for higher current applications.
FAQs
What are the sizes of glass and ceramic fuses?
OptiFuse offers a variety of sizes for glass and ceramic fuses, with the most common being:
3.6x10m Fuses / 5x15mm Fuses / 5x20mm Fuses / 6.3x32mm Fuses / 10x38mm Fuses (Industrial Size)
How can you tell if a glass/ceramic fuse is blown?
To tell if a glass or ceramic fuse is blown, start with a visual inspection for glass fuses; look through the transparent body to see if the internal metal link is broken or melted. For ceramic fuses, visual inspection won't work, so it's best to use a multimeter or dedicated fuse tester to check for continuity and confirm whether the fuse is still functional.
Can I replace a ceramic fuse with a glass fuse?
It is generally not recommended to replace a ceramic fuse with a glass fuse due to their differing properties and performance characteristics. Ceramic fuses are designed to handle higher currents and temperatures, and they offer better arc-quenching capabilities because of their sand-filled structure. In contrast, glass fuses may not withstand the same level of electrical stress. If you consider replacing a fuse with one that is not listed by the manufacturer as an acceptable substitute, it is advisable to consult an electrical professional to ensure that you meet the protection requirements for your circuit.
What happens if you use a lower amp or volt fuse?
Using a fuse that is not rated to meet the needs of your system can lead to several issues. First, a fuse with a lower amp rating may blow frequently during normal operation because it cannot handle the circuit's required current, resulting in constant interruptions and downtime. Additionally, if the voltage rating is lower than necessary, the fuse may not effectively protect against overcurrent situations, potentially allowing excessive current to pass through and causing damage to connected equipment. Furthermore, using an undersized fuse can generate excessive heat, increasing the risk of fire or damage to wiring and components.
See Also
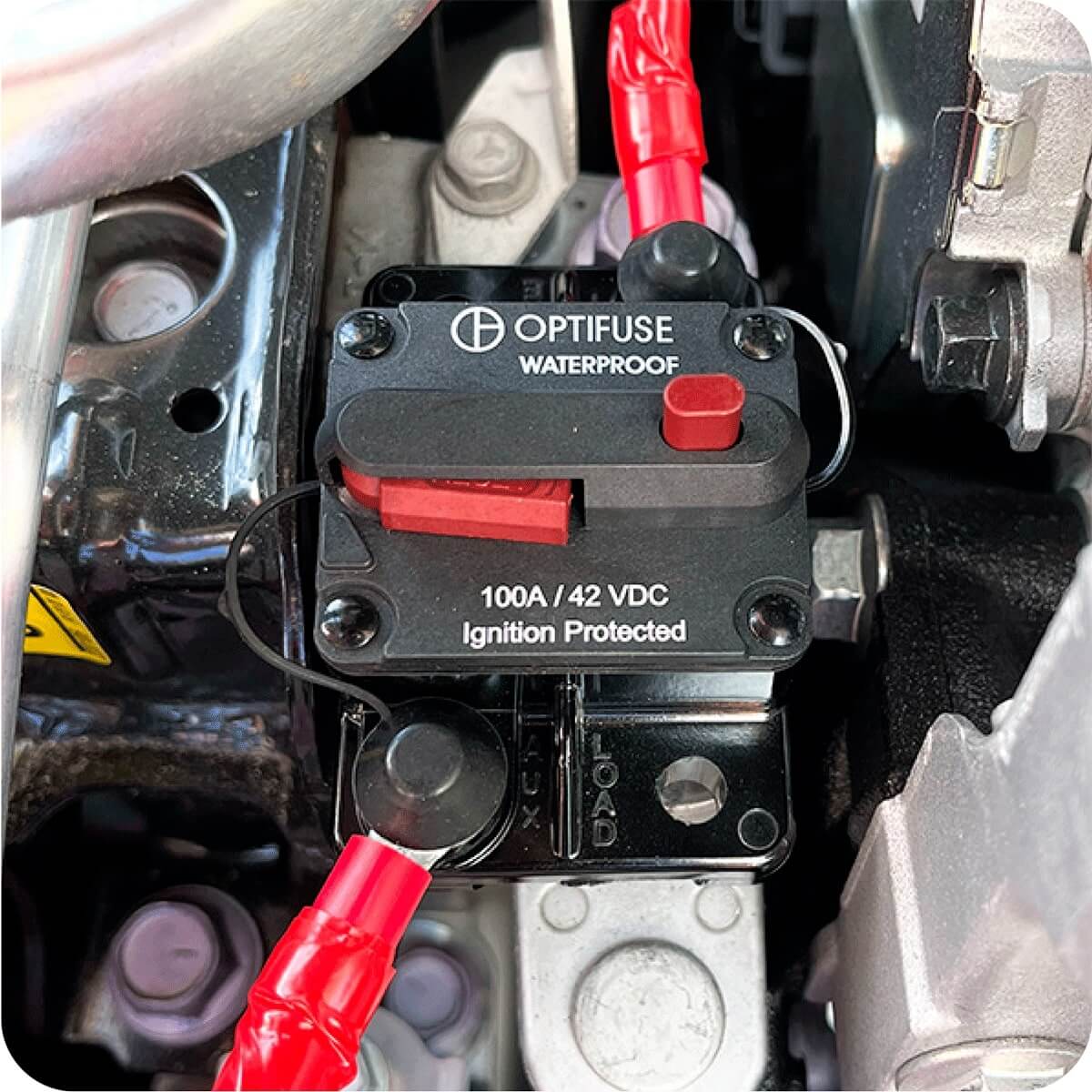

Circuit Breakers
A comprehensive range of automotive, marine grade and line voltage circuit breakers to protect applications where resettability is needed.
Fuse Holders, Blocks and Accessories
Installing circuit protection is easy with our wide variety of customizable fuse holders, sturdy fuse blocks, and compact fuse clips.