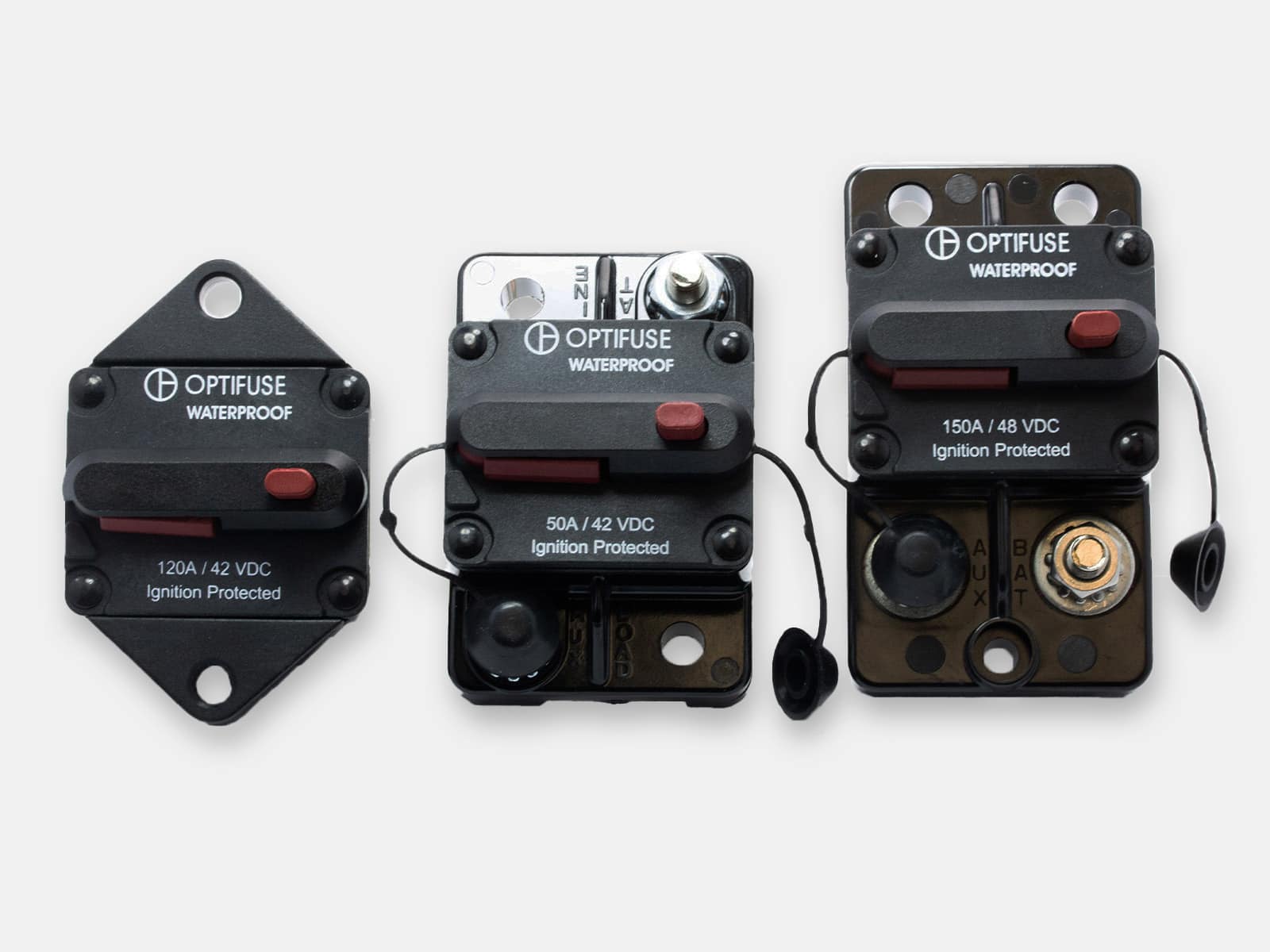
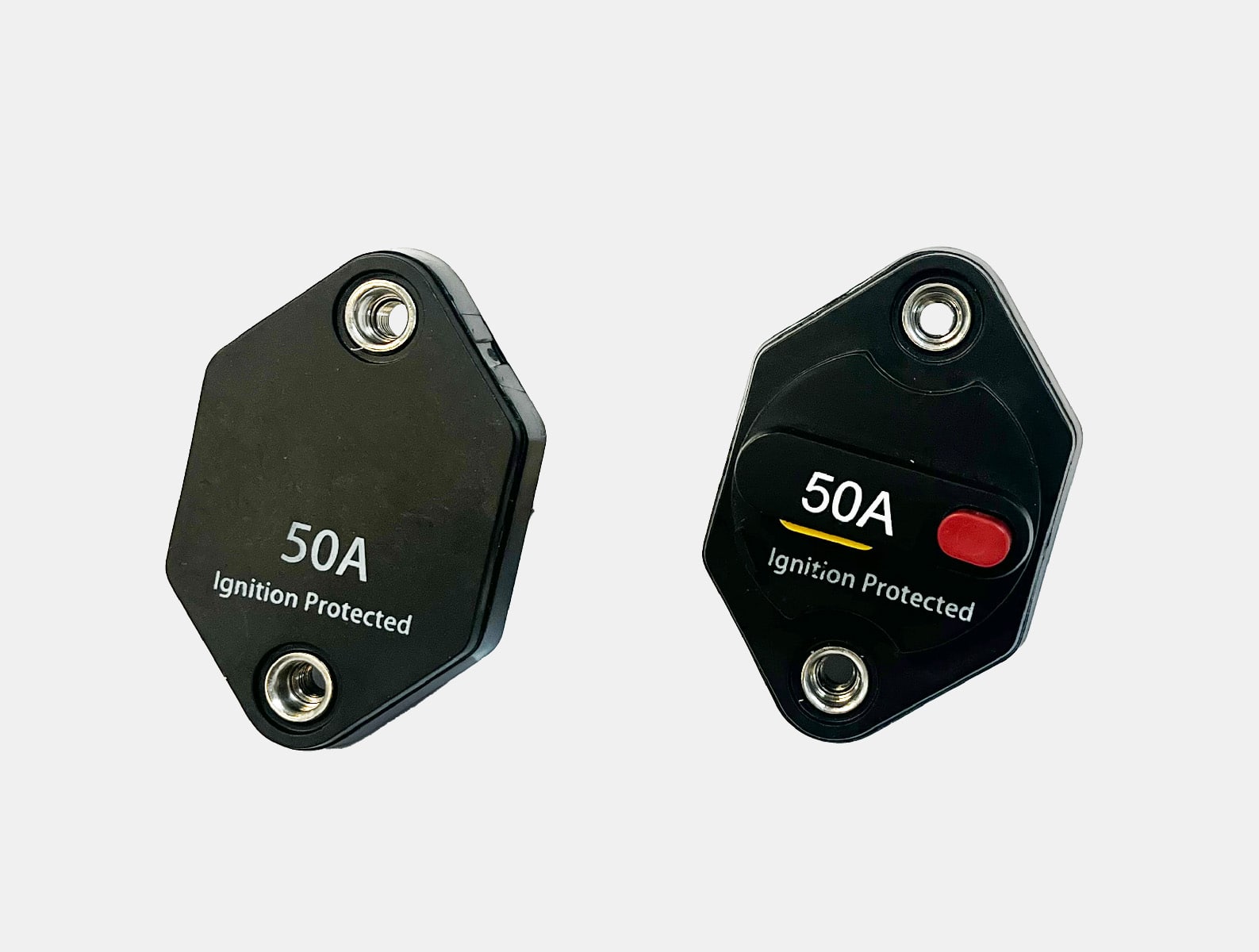
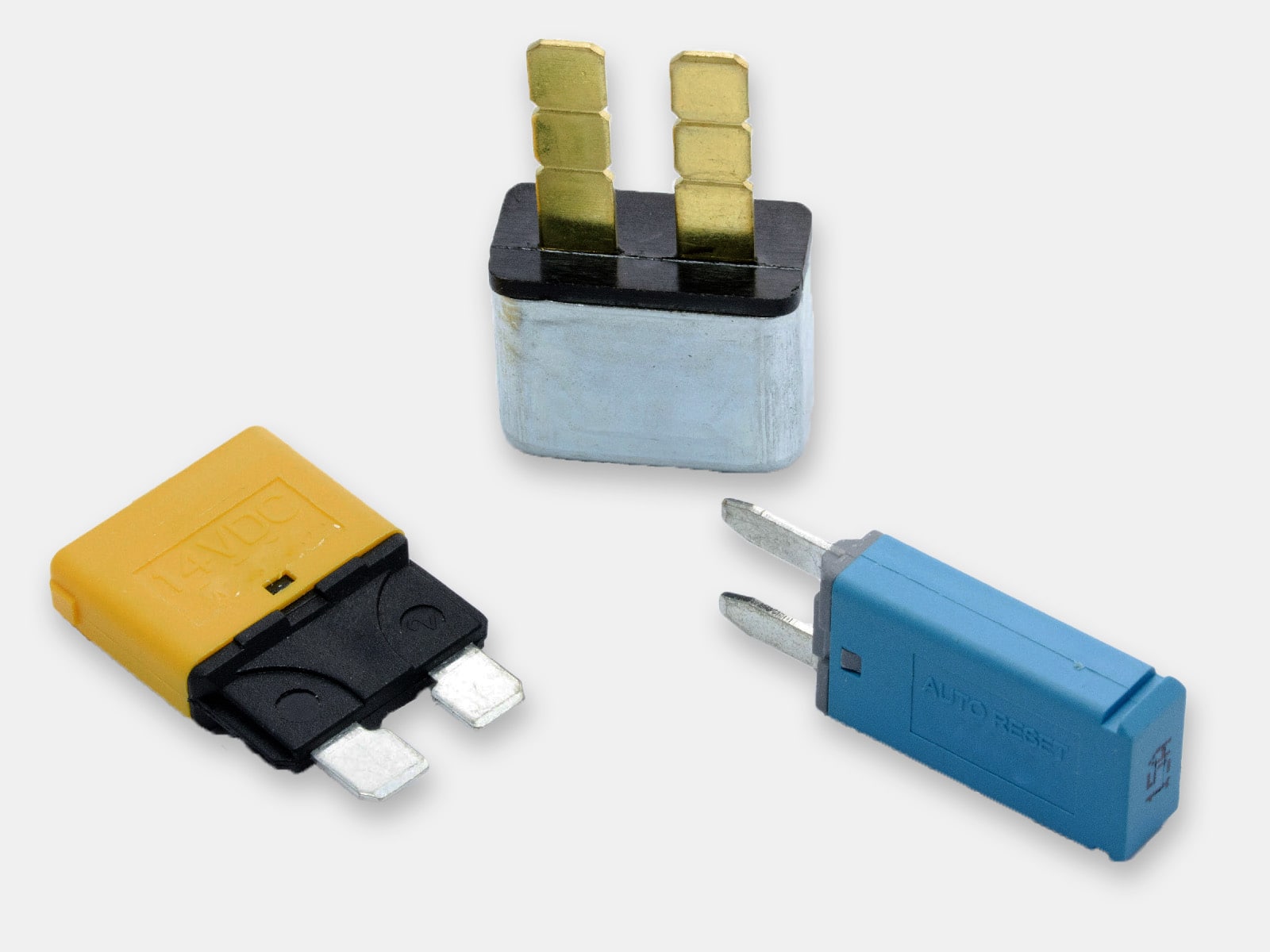
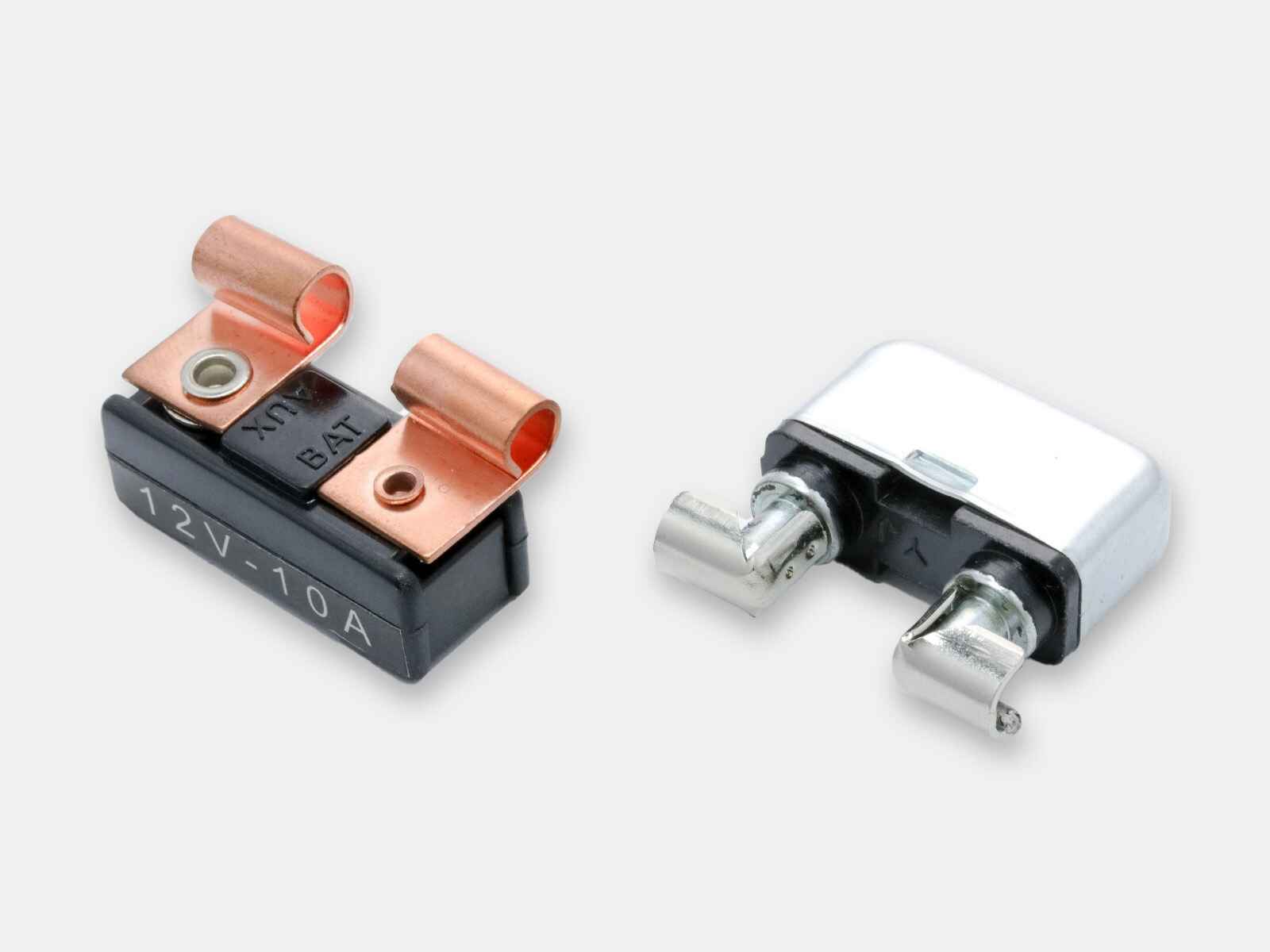
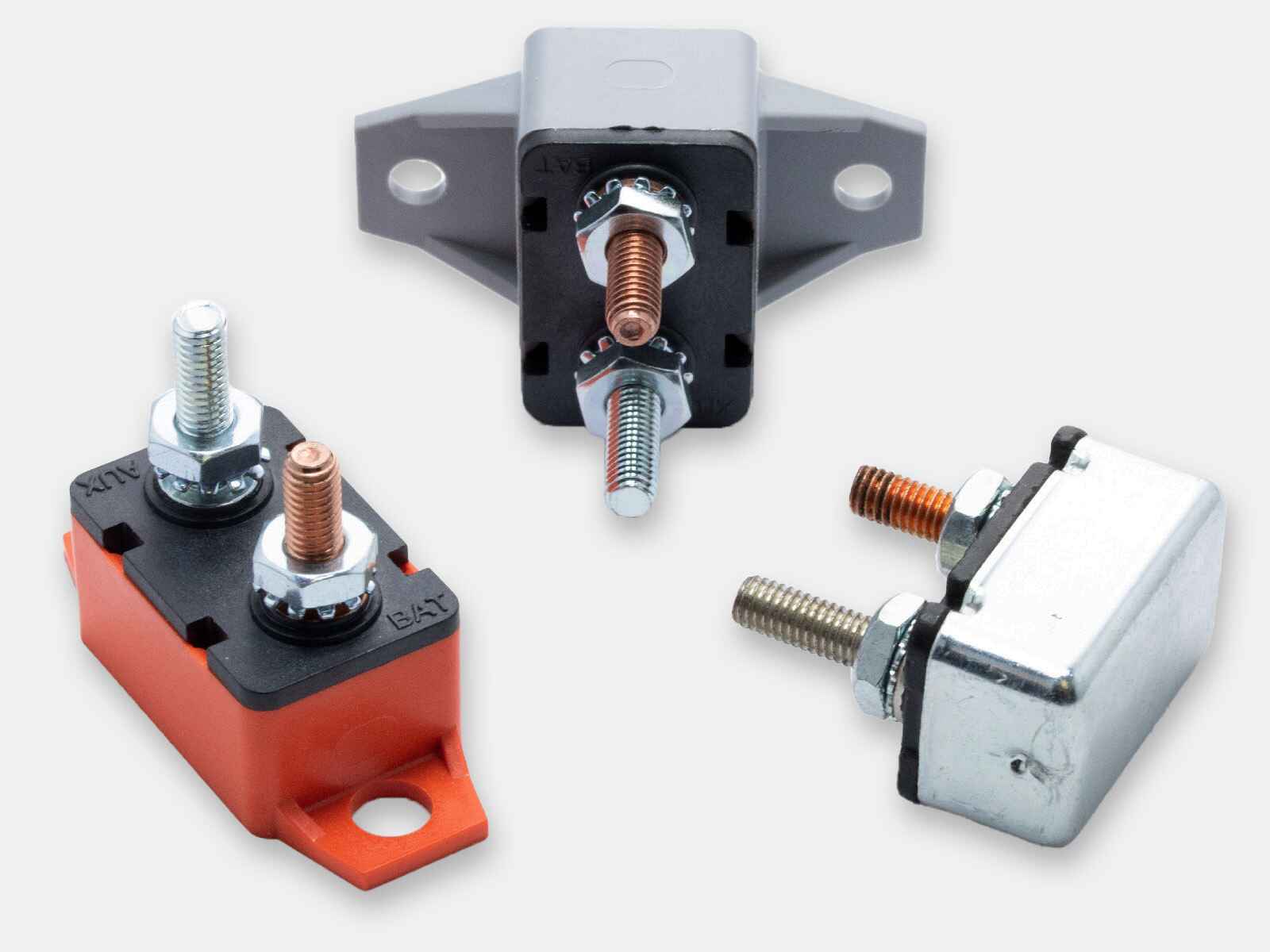
Circuit breakers manufacturer and distributor

Circuit breakers have switch mechanisms that trip at the onset of unsafe surges of electricity. They can be repeatedly tripped and reset in the event of overcurrents and do not need to be replaced after each use like fuses do. Depending on which type you choose, the breaker while either reset itself automatically or will require you to manually reset it in order to restart the flow of electricity following an overcurrent event. OptiFuse offers a comprehensive range of automotive, marine grade and line voltage circuit breakers to protect your application where resettability is needed.
Discover our selection of circuit breakers
Useful Resources
Knowledge Center
Circuit breaker: What is it?
A circuit breaker is an electrical protection device designed to automatically stop the flow of electricity when a fault, such as an overload or short circuit, occurs in a circuit. Unlike fuses, which must be replaced once they blow, circuit breakers can be reset after they trip, allowing them to be reused.
The importance of circuit breakers
Circuit breakers are important because they protect electrical systems from dangerous overcurrents, preventing damage to components, overheating, and fires. They ensure that the wiring does not melt, safeguarding the overall system and enabling safe operation.
What are the different types of circuit breakers?
There are three main types of circuit breakers based on how they reset:
- Type I – Automatic Reset Circuit Breakers: Automatically reset after tripping, ideal for situations where overloads are infrequent, and manual access is limited.
- Type II – Modified Reset Circuit Breakers: Require the system to be powered off to reset, used in systems needing protection only when powered on.
- Type III – Manual Reset Circuit Breakers: Must be manually reset after tripping, useful for identifying and addressing system issues before restoring power.
What is the difference between circuit breakers and fuses?
The primary difference between circuit breakers and fuses is that circuit breakers are resettable and reusable, while fuses need to be replaced after each trip.
What does an automotive circuit breaker do?
An automotive circuit breaker protects the vehicle’s electrical system by interrupting the current flow when it detects a dangerous level of current. This prevents damage to wiring and components by disconnecting power to affected circuits. The breaker automatically resets after tripping, allowing the circuit to be restored once the issue is resolved.
What is the difference between DC breaker and AC breaker?
AC breakers and DC breakers differ in their design and applications:
- DC Breakers: Designed for direct current systems, such as those in automotive applications. They handle continuous current flow and higher arcing potential.
- AC Breakers: Designed for alternating current systems, commonly used in industrial settings. They benefit from natural current zero crossings to extinguish arcs more easily.
Understanding the specific requirements of your system is crucial when choosing between AC and DC breakers.
How do you reset your breaker?
Resetting your breaker depends on which type of circuit breaker you are using:
- Type I – Auto Reset Circuit Breakers: Automatically reset themselves after tripping.
- Type II – Modified Reset Circuit Breakers: Require you to turn off the system to reset. They will reset automatically once the system is powered off and back on.
- Type III – Manual Reset Circuit Breakers: Must be manually reset by pushing a lever or button after tripping.
Can a circuit breaker reset itself automatically?
Yes, Type I circuit breakers automatically reset themselves after being tripped.
What are the signs of a bad circuit breaker?
The most common sign of a bad circuit breaker is frequent tripping, which may occur due to age or overuse. Other signs include the breaker being hot to the touch, showing physical damage like scorch marks or frayed wires, or making a humming noise. If any of these signs are present, the breaker may need to be replaced.
What amp circuit breaker should I use for my application?
For your application, choose a circuit breaker sized to 135% of the full-load steady-state current of your circuit. If this calculation does not match a standard breaker size, use the next available size up. For example, for a 10A circuit, you need a 13.5A breaker (10A × 135%). Since 13.5A is not a standard size, use a 15A breaker.
See Also

Fuses
Many styles of innovative, versatile fuses are available to protect circuits from dangerous overcurrents in automotive, electronic, and industrial applications.
Fuse Holders, Blocks and Accessories
Installing circuit protection is easy with our wide variety of customizable fuse holders, sturdy fuse blocks, and compact fuse clips.